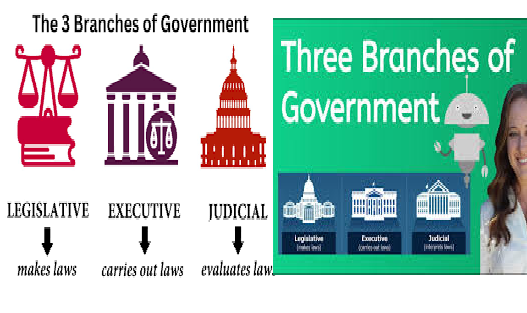
What are the 3 branches of government? This is a common question for understanding the foundation of governmental systems worldwide. The three branches of government, established to provide checks and balances, are the Legislative, Executive, and Judicial branches. Each plays a unique role in governance, ensuring no single branch gains excessive power. Let’s explore the roles and leaders within these branches, including examples from the United States and Pakistan.
1. Legislative Branch
The Legislative Branch is responsible for creating laws. In the U.S., Congress—comprising the House of Representatives and the Senate—fulfills this role. Legislators debate, draft, and pass laws that shape national policy.
In Pakistan, the legislative authority lies with the Parliament, which consists of the National Assembly and the Senate. Members of the legislative branch are either elected or appointed and represent the people’s voice in government.
2. Executive Branch
The Executive Branch enforces laws and administers government functions. In the U.S., the President leads this branch, serving as both the head of state and government. The President is supported by the Vice President, chosen through an electoral process along with cabinet members who oversee various departments. The Vice President’s role complements the President, and both are selected through a national election.
In Pakistan, the Prime Minister is the head of the Executive Branch, supported by the Executive Minister and other ministers appointed to various departments. The executive branch of Pakistan also includes the President as a ceremonial leader, while the Prime Minister holds the executive power. The role of the Executive Branch in both countries involves implementing laws, handling foreign policy, and guiding the nation’s administrative actions.
3. Judicial Branch
The Judicial Branch interprets laws and ensures justice is upheld. In the U.S., the Supreme Court is the highest authority in the Judicial Branch, reviewing cases and evaluating laws’ constitutionality. Judges are appointed to maintain impartiality in interpreting the law.
In Pakistan, the judiciary is headed by the Chief Justice, with the Supreme Court acting as the ultimate authority in legal matters. The Judicial Branch provides checks and balances on the Legislative and Executive branches, ensuring that all actions comply with the constitution.
Three Pillars of Government in Pakistan
In Pakistan, the government is built on three main pillars: the Legislative, Executive, and Judicial branches. These branches form the basis of governance, creating a balance of power and responsibilities similar to those in the U.S. The Parliamentary system in Pakistan means that the Prime Minister, who is part of the legislative body, also acts as the head of the Executive Branch, thus integrating some responsibilities across branches while maintaining checks and balances through the judiciary.
The Main Responsibilities of the Federal Government
The federal government in any country generally focuses on three primary responsibilities:
- National Defense and Security: Protecting the country’s borders and maintaining peace.
- Public Services: Providing essential services such as healthcare, education, infrastructure, and social welfare.
- Economic Stability and Regulation: Managing the economy through policies, taxation, and regulation of trade and commerce.
These responsibilities are central to a government’s role in maintaining stability, growth, and public welfare.
Who Chooses the Vice President?
In the United States, the Vice President is chosen alongside the President during national elections. The candidate for Vice President runs on a joint ticket with the presidential candidate, and voters indirectly choose the Vice President through the electoral process.
In parliamentary systems like Pakistan, there isn’t a direct equivalent to the Vice President, but the Prime Minister is supported by cabinet ministers and other officials in executing duties, with the President serving a ceremonial role.
Understanding what are the 3 branches of government and their functions provides insight into how different nations structure governance to balance power, safeguard citizens, and uphold justice. Each branch, whether in the U.S., Pakistan, or other countries, has its unique responsibilities that collectively ensure a stable and fair government.
Read more:
1= https://rapidurlindexer.net/blogs/what-are-the-3-main-credit-bureaus/
2= https://rapidurlindexer.net/blogs/what-are-the-3-most-important-branches-of-government-called/
3= https://rapidurlindexer.net/blogs/what-are-the-worst-side-effects-of-prednisone/